Data manipulation
Introduction to dplyr (package in the tidyverse)
Review
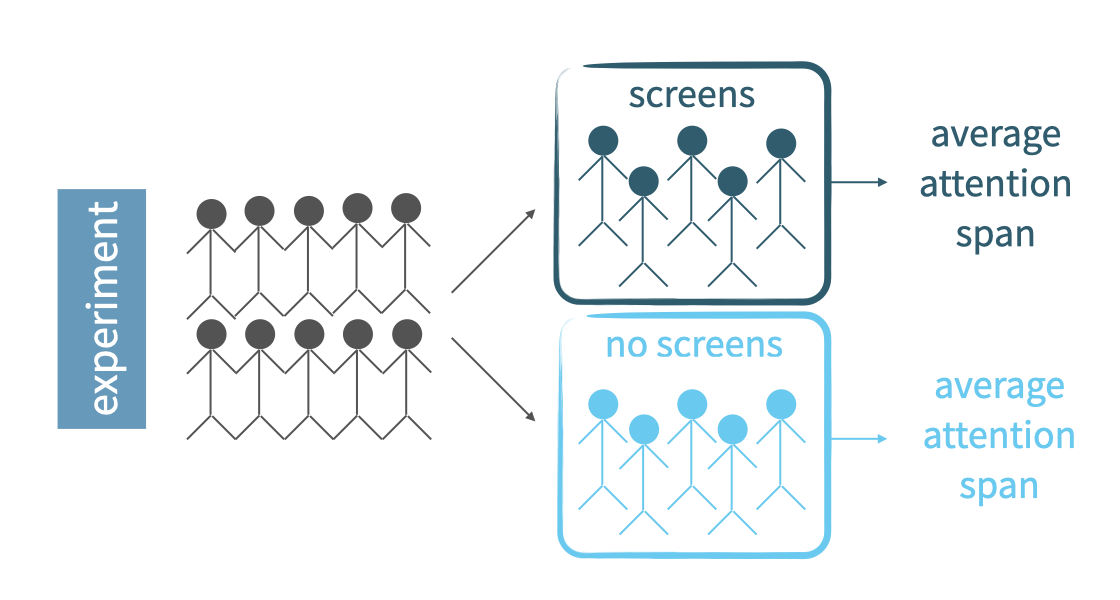
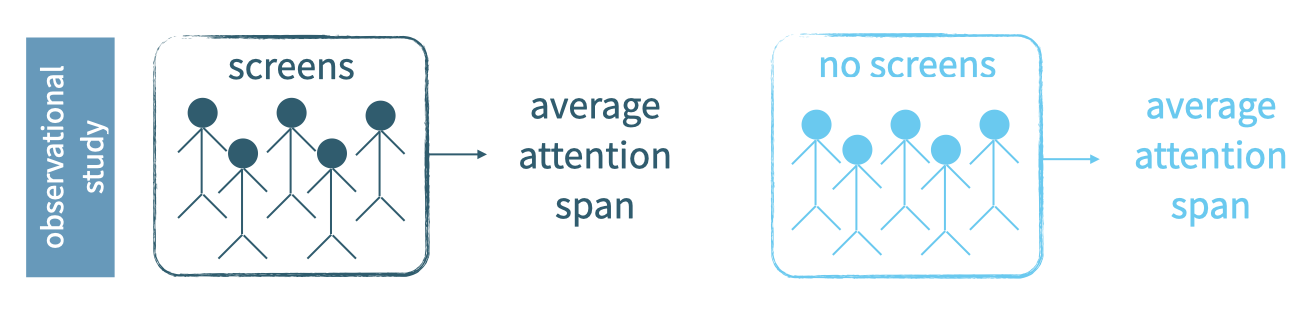
- types of data collection
- experimental vs observational
- tidy data
- variables
- explanatory vs response variables
- associated vs independent
- type numeric vs categorical
- summary statistics
- target population
- census vs sample
- sample statistic vs population parameter
- random sampling and random assignment
Review: experimental vs observational
Data transformation with dplyr
dplyris a powerful R package for data manipulation.one of the packages in the tidyverse
Provides a coherent set of verbs functions to help you resolve most data manipulation challenges
Using dplyr
-
expects tidy data
each variable in its own column
each observation in its own row
-
works with pipes |> (or %>% )
- x |> f becomes f(x, y)
-
|> take something as input for next command
- “then”
Data transformation with dplyr
first argument is a data frame
subsequent arguments describe what to do with the data frame
result is a new data frame
Key functions in dplyr
function() |
Action |
|---|---|
glimpse() |
get a glimpse of your data |
count() |
count the unique values of one or more variables |
filter() |
picks rows based on their values |
mutate() |
creates new variables (columns) |
select() |
picks variables (columns) |
summarize() |
reduces multiple values down to a single statistic |
arrange() |
changes the order of the rows based on their values |
group_by() |
create subsets of data to apply functions to |
Outline
Functions we will cover today:
glimpse()count()
Load the packages and data
- cars93 is part of the
openintropackage - type
?cars93for the help page
cars93 data frame is tidy
Each row is a car (observation)
Variables (columns) contain information on a car
Variables
type- levels large, midsize, and smallpricempg_citydrive_train- levels 4WD, front, and rearpassengersweight
Glimpse
fctrefers to categories or levels of dataintanddblrefer to “integer” and “double” or numerical data
- Which variables in
cars93are- numerical (int or dbl)
- categorical or categorical (fct)
Rows: 54
Columns: 6
$ type <fct> small, midsize, midsize, midsize, midsize, large, large, m…
$ price <dbl> 15.9, 33.9, 37.7, 30.0, 15.7, 20.8, 23.7, 26.3, 34.7, 40.1…
$ mpg_city <int> 25, 18, 19, 22, 22, 19, 16, 19, 16, 16, 21, 17, 20, 20, 29…
$ drive_train <fct> front, front, front, rear, front, front, rear, front, fron…
$ passengers <int> 5, 5, 6, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5, 6, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 6, 5, 6, 4…
$ weight <int> 2705, 3560, 3405, 3640, 2880, 3470, 4105, 3495, 3620, 3935…Count the number of observations for each type
| type | n |
|---|---|
| midsize | 22 |
| small | 21 |
| large | 11 |
- Which car
typehas the highest number of observations?
Your Turn - count
Which drive_train has the highest number of observations?
Filter
picks rows based on their values
Filter: comparison operators
==equality>greater than<less than>=greater than or equal to<=less than or equal to!=not equal tobetweennumeric variable in a specified rangenearcompare 2 numeric vectors. Set tolerance
Filter
Combine criteria using operators that make comparisons:
|or&and,
Filter - extract observations (rows)
| type | price | mpg_city | drive_train | passengers | weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| midsize | 33.9 | 18 | front | 5 | 3560 |
| midsize | 37.7 | 19 | front | 6 | 3405 |
| midsize | 30.0 | 22 | rear | 4 | 3640 |
| midsize | 15.7 | 22 | front | 6 | 2880 |
| midsize | 26.3 | 19 | front | 5 | 3495 |
| midsize | 40.1 | 16 | front | 5 | 3935 |
| midsize | 15.9 | 21 | front | 6 | 3195 |
| midsize | 15.6 | 21 | front | 6 | 3080 |
| midsize | 20.2 | 21 | front | 5 | 3325 |
| midsize | 13.9 | 20 | front | 5 | 2885 |
| midsize | 47.9 | 17 | rear | 5 | 4000 |
| midsize | 28.0 | 18 | front | 5 | 3510 |
| midsize | 35.2 | 18 | rear | 4 | 3515 |
| midsize | 34.3 | 17 | front | 6 | 3695 |
| midsize | 61.9 | 19 | rear | 5 | 3525 |
| midsize | 14.9 | 19 | rear | 5 | 3610 |
| midsize | 26.1 | 18 | front | 5 | 3730 |
| midsize | 21.5 | 21 | front | 5 | 3200 |
| midsize | 16.3 | 23 | front | 5 | 2890 |
| midsize | 18.5 | 19 | front | 5 | 3450 |
| midsize | 18.2 | 22 | front | 5 | 3030 |
| midsize | 26.7 | 20 | front | 5 | 3245 |
Your Turn
Extract the cars that have front drive_train
Your Turn
Extract the cars that are type large AND have 4WD drive_train
Your Turn
Extract the cars that are type large OR have 4WD drive_train
Summary
glimpse()count()
Quiz
One question on a dataset from an OpenIntro Data Set
Seven questions on
dplyrfunctions
